Type 2 Diabetes: Understanding and Managing the Condition
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition where the body either resists insulin or doesn’t produce enough, leading to high blood sugar. Over time, this can result in complications like heart disease, kidney damage, nerve issues, and vision problems.
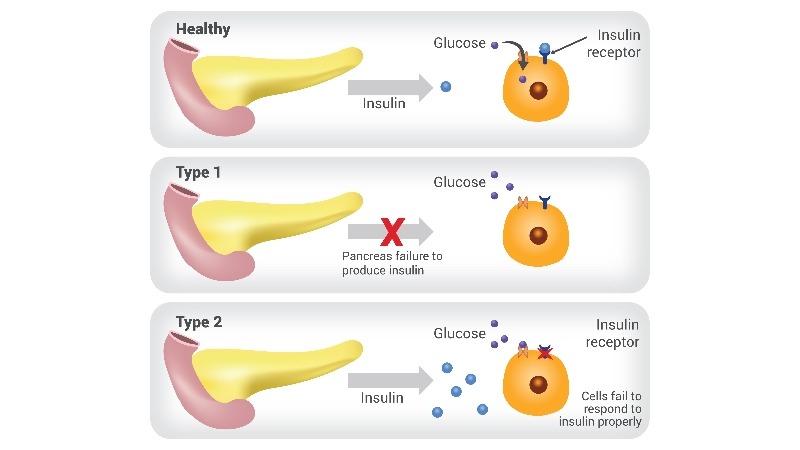
Key Factors
- Insulin Resistance: Cells fail to respond to insulin properly.
- Impaired Insulin Production: The pancreas struggles to produce sufficient insulin.
- Lifestyle and Genetics: Poor diet, lack of exercise, obesity, and family history contribute significantly.
Common Symptoms
- Excessive thirst and frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss and fatigue
- Blurry vision and slow-healing wounds
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
Risk Factors
- Age (especially over 45)
- Family history of diabetes
- Obesity and inactivity
- Poor diet
Treatment and Management
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopt a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and manage weight.
- Medications: Includes oral drugs like metformin or insulin injections.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regular checks to maintain stable levels.
Reversing Type 2 Diabetes: Is it Possible?
While reversal is not a permanent cure, it involves achieving normal blood sugar levels without medication through dietary and lifestyle changes.
Key Strategies
1. Achieve a Healthy Weight
- Why: Weight loss improves insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
- How: Focus on nutrient-dense, low-calorie foods to encourage sustainable weight loss.
2. Reduce Carbohydrates
- Why: Carbs, especially refined ones, spike blood sugar.
- How: Prioritize low-glycemic, high-fiber carbs like vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
3. Increase Fiber Intake
- Why: Fiber slows glucose absorption and boosts insulin sensitivity.
- How: Eat high-fiber foods like vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains.
4. Incorporate Healthy Fats
- Why: Omega-3 fats reduce inflammation and enhance insulin function.
- How: Include fats from olive oil, avocado, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
5. Eat Regular, Balanced Meals
- Why: Prevents blood sugar fluctuations.
- How: Consume smaller, balanced meals throughout the day.
6. Adopt a Low-Glycemic Index (GI) Diet
- Why: Low-GI foods raise blood sugar gradually.
- How: Choose whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables.
7. Explore Intermittent Fasting
- Why: Improves insulin sensitivity and aids weight loss.
- How: Try time-restricted eating, like 16:8 fasting, under professional guidance.
8. Avoid Processed Foods & Sugary Drinks
- Why: They cause rapid blood sugar spikes.
- How: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods and avoid sugary drinks/snacks.
9. Increase Plant-Based Foods
- Why: These are rich in fiber and antioxidants, supporting blood sugar control.
- How: Incorporate more vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains.
10. Include Supportive Nutrients
- Why: Magnesium, chromium, and vitamin D help regulate blood sugar.
- How: Ensure adequate nutrient intake through diet or supplements.
11. Be Consistent & Monitor Progress
- Why: Regular tracking ensures dietary changes are working.
- How: Monitor blood sugar levels and adjust your diet as needed.
Comprehensive Approach to Reversal
Diet is foundational, but combining it with:
- Nutritional Support: Adequate vitamins and minerals.
- Stress Management: Reducing cortisol levels.
- Proper Sleep: For overall metabolic health.
📞 Contact us today for personalized guidance and support!

