Leaky Gut: What You Need to Know
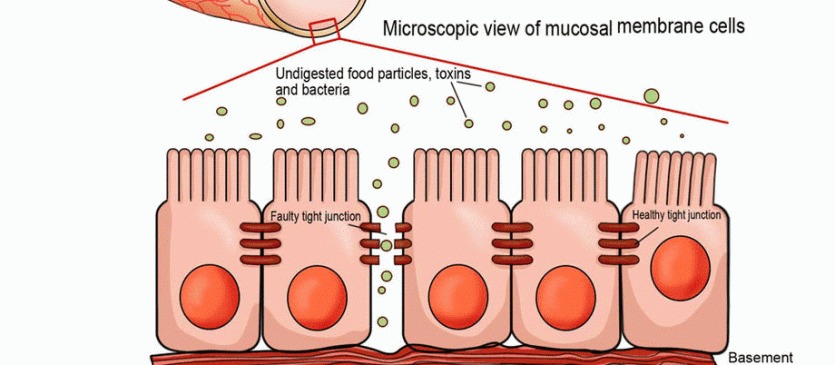
Leaky gut occurs when the small intestine's lining is damaged, creating gaps between cells. This allows undigested food, toxins, and bacteria to "leak" into the bloodstream, leading to inflammation, immune reactions, and a host of health issues.
Symptoms of Leaky Gut
- Digestive Issues: Bloating, gas, diarrhea, constipation, or IBS.
- Food Sensitivities: Allergies to gluten, dairy, etc.
- Chronic Fatigue: Tiredness that doesn’t go away with rest.
- Joint Pain: Inflammation similar to arthritis.
- Skin Problems: Acne, eczema, psoriasis.
- Brain Fog: Difficulty focusing or memory problems.
- Headaches: Frequent migraines or tension headaches.
- Autoimmune Conditions: Worsening of existing autoimmune disorders.
How to Heal Leaky Gut
1. Diet
- Follow an anti-inflammatory diet: Avoid processed foods, sugar, gluten, and dairy.
- Eat nutrient-dense, whole foods.
2. Gut-Healing Foods
- Bone broth, collagen, fermented foods (sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir), and prebiotics (garlic, onions).
3. Probiotics
- Include probiotic supplements or foods to restore gut bacteria balance.
4. Stress Management
- Practice exercise, meditation, yoga, or relaxation techniques.
5. Supplements
- Consider L-glutamine, zinc, and digestive enzymes.
6. Avoid Harmful Substances
- Limit NSAIDs, antibiotics, and medications that can damage the gut lining.
Why Be a Sick Person? Change Your Story!
✨ Take charge of your health today!
📞 Get in touch to learn how we can help you on this journey.
How Long Does Healing Take?
- Most cases see improvement within 3 months, but it can take longer depending on individual factors.
(Add this to a visual calendar with “3 months” highlighted.)
When Healing May Require Additional Support
In some cases, diet alone may not fully reverse leaky gut. Medical intervention may be required for:
- Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD): Medication like immunosuppressants may be necessary.
- Celiac Disease: A strict gluten-free diet is essential, but recovery depends on continued compliance.
- Severe Gut Dysbiosis or SIBO: Antibiotics or specific probiotics might be needed.
- Chronic Stress or Trauma: Stress management or therapy can be critical.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Additional medical treatment to regulate immune responses may be required.
- Chronic Infections: Treatment for H. pylori or other infections may involve antimicrobial therapies.
- Toxic Exposure: Detoxification programs may be required for mold or heavy metal exposure.
- Maldigestion or Pancreatic Insufficiency: Enzyme supplements or digestive aids may be necessary.
- Undiagnosed Health Issues: Conditions like diabetes, thyroid imbalances, or liver disease require specific medical attention.
- Medications: Long-term use of certain drugs may need careful adjustment and medical oversight.
💡 Tip: Combining diet with medical treatments can enhance results and speed recovery.

